
The oral intake for DEHP in classrooms and the dermal intake of DnBP and DiBP in homes are the highest. The total daily intake of DEHP, DnBP, and DiBP ranges from 97.3 to 336 ng/ (kg The differences in the phthalate concentrations between sunny and shaded rooms and urban and suburban classrooms are insignificant, whereas that between male and female dormitories is significant. The PMF results indicated that two, four, and three types of phthalate sources exist in home, dormitory, and classroom, respectively. The median proportion of DEHP in dust is the highest, ranging from 67.1 to 72.9%. Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), di-n-butyl phthalate (DnBP), and di-isobutyl phthalate (DiBP) are the most abundant phthalates. The detection frequency of eight phthalates in dust ranges from 74.5 to 100%. In addition, we estimated the daily intake of phthalates via three pathways using Monte Carlo simulations. We analyzed the characteristics of phthalates in dust from three environments. It provides objective data for decision making.The phthalate concentrations in dust from undergraduate dormitories, classrooms, and homes in Beijing, China, were measured in April 2017.Quantifies risks to assess impacts better.Predicts the likelihood of schedule and cost overruns.It creates a more realistic budget and schedule.It provides early identification of how likely you are to meet project milestones and deadlines.Benefits of using Monte Carlo analysis on your projects are: Monte Carlo simulation is a data-driven approach to quantify risk, understand project risks, predict outcomes. Microsoft Excel provides statistical functions to perform Monte Carlo simulation. The output reveals the range of possible outcomes, their probability of occurring. These tools simulate thousands of different “what if” cases, saving the inputs and results of each calculation as individual scenarios. uniform if the activity has a high probabilityĬrystal Ball from Oracle, Risk from PALISADE, Sim Tools are few popular tools to perform Monte Carlo simulations in your Excel spreadsheets and models.asymmetric triangular or beta if the activity has a medium probability.symmetric triangular or beta if the activity has a low probability.To choose the type of statistical distribution, we have to consider the qualitative risk analysis for the activity: To consider risk, activities are modeled with three points: optimistic, pessimistic and most likely. See the following table with activity duration estimates.
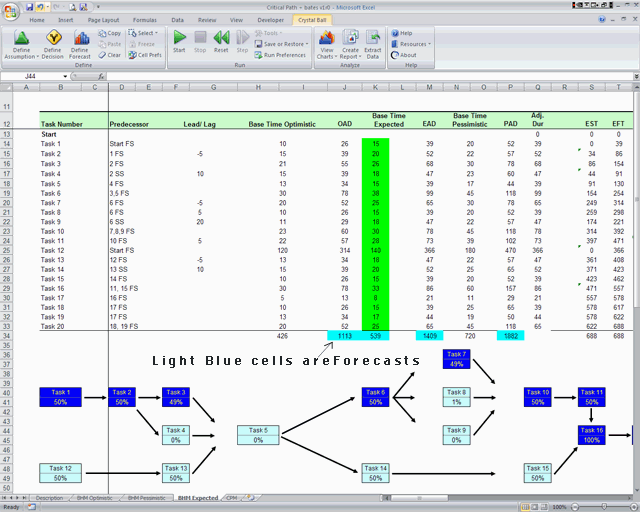
The book uses a case study of a tennis stadium construction project. Regarding Monte Carlo’s analysis, you can model them as no-risk activities. If the activity is a black swan –beyond the expected situation, very low probability, very high impact– you can manage them as assumptions.If the activity has an unknown risk –the project manager doesn’t have the proper knowledge to produce a reliable estimate– you can set a range of possible values and model the activity as a uniform distribution.If the activity has a known risk –causes of variances are well known and the project management team knows the activity will be earlier or later if causes happen– then you can use an asymmetric beta or triangular.If the activity has low risk –estimation is quite precise except for unexpected variations due to random factors– you can use asymmetric beta or triangular.
You can model the activity with the most likely estimate.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
